The chemical processing industry (CPI) is one of the largest industry segments in the world. CPI is broadly defined as the chemical conversion of raw materials to finished products. Subsectors of CPI include:
- Traditional chemicals, both organic and inorganic
- Petroleum
- Petrochemical
- Refining
- Pharmaceutical facilities
- Marine support and offshore
The chemicals market, according to Chemical Processing, is currently worth around $1 trillion and is projected to grow to more than $5 trillion by 2022. With 40,000 facilities currently in operation and thousands more in the queue, optimizing new builds and repairs with the most efficient, cost-effective materials possible is imperative to the success of each application.
Material Options
Piping in chemical processing plants is subjected to some of the most challenging industrial environments. Chemical processing operating conditions often involve aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, which often cause corrosion, process leaks and premature failures.
Many plants traditionally use alloys, such as carbon steel or stainless steel, due to their inherent strength and the industry’s familiarity with their performance—both the strengths and weaknesses. Misapplication of these materials can lead to regular replacement every few years. And as the chemical industry continues to specialize in advanced chemistries, the need for piping materials that can handle the full pH range grows.
By specifying alternative materials ideally suited for chemical processing applications, systems can operate reliably for decades, resulting in material cost savings, installation cost savings and less downtime.
A Reliable Choice
In many applications, plants have found a cost-effective, reliable alternative in chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) piping. CPVC has become an industry standard material satisfying the need for reliable piping systems and providing the balance between performance and costs.
Commercialized by Lubrizol nearly 60 years ago, CPVC is a thermoplastic specially engineered for the harsh conditions of chemical processing applications. It offers excellent corrosion resistance to a broad range of chemicals, and better impact strength and temperature resistance than many other nonmetallic materials.

Lubrizol continues to lead the CPVC market with its Corzan® CPVC technology. Today, it is the most specified industrial CPVC material in the world. It has become a staple of chemical processing applications. Due to its extensive chemical resistance, elevated temperature resistance and suitable pressure performance, there have been a growing number of successful installations in CPI applications across the world.
Why CPVC for the Chemical Processing Industry?
The most important quality for piping in demanding chemical applications is suitability. Put simply, is a given piping material compatible with the process—including its chemicals, temperature demands and pressure requirements—so that it can last for decades without replacement?
CPVC provides several advantages that make it suitable for a variety of chemical processing applications:
- Eliminates internal and external corrosion caused by many corrosive chemicals.
- Significantly lowers life-cycle costs compared to metallic systems and requires significantly less maintenance than many other plastics.
- Ensures optimal flow rates with excellent hydraulic capabilities and pressure ratings up to 200°F (93.3°C)—nearly 80°F (45°C) higher than PVC.
- Achieves long-term performance with excellent mechanical strength, and Corzan CPVC has the highest impact resistance (24448 cell class for pipe available up to 8 in., as defined by ASTM-D1784) of any CPVC pipe compound.
Corrosion resistance is an especially important advantage of CPVC, as the material inherently withstands corrosion from a wide range of acids, bases and salts, even at elevated temperatures. Some notable CPI chemicals it is compatible with include:
- Sodium hypochlorite
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulfuric acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Sodium chloride
- Caustic soda
This extensive corrosion resistance enables CPVC use across plants for pure chemical streams, and also waste streams, depleted streams and treatment streams.
To see Corzan CPVC’s compatibility with more than 400 chemicals, view the Chemical Resistance Table.
Installation is another important aspect of piping material selection. In many cases, installation accounts for more than half of the overall system costs. CPVC is different because it:
- Decreases total installation costs attributed to lower material costs and installation time, as compared to metallic alternatives.
- Is lightweight (1/8 the weight of steel), reducing the additional equipment needed to move the piping.
- Can be installed without welding equipment, eliminating the need for torches, complicated heat-fusion techniques and hot-welding permits.
- Reduces downtime during repairs, as mechanical couplings can be easily used to join the pipe and immediately reboot the system.
- Can be joined with solvent cement welding, which often becomes the strongest part of the system (whereas most material joining techniques make joints the weakest part).
Some other notable advantages that address the concerns plant engineers and managers may have about a thermoplastic piping material is that Corzan CPVC:
- Is specially engineered to withstand weathering from UV light.
- Comes in diameters up to 24-in. (check with each manufacturer).
- Meets and exceeds regulatory requirements, including smoke and flame resistance and NSF International standards for potable water safety.
- Minimizes total system costs and price uncertainty with stable material prices.
- Has low flame, smoke and toxicity ratings, meeting International Maritime Organization (IMO) 753 (international maritime organization) guidelines as well as the United States Coast Guard (USCG) requirements.
- Meets the 25/50 low flame and smoke requirements of CAN/ULC 102.2 requirements for use in return are plenums.
Where Can CPVC Be Used in Chemical Processing Plants?
With a wide chemical resistance range, superior performance attributes and extensive approval across key industry standards, CPVC is frequently specified in the following chemical processing applications:
- Potable water
- Reclaimed water
- Eye wash and shower stations
- Demineralized/Reverse Osmosis (DI/RO) water
- Condensate water transfer
- Facility unloading stations for key acids and bases
- Facility distribution
- Process transfer lines or injection lines for acids and bases
Potable Water
In potable water treatment systems, contaminated water from rivers, lakes and reservoirs is altered to an acceptable drinking state. The incoming water, which may have a high content of minerals, metal, chloride or particulates, is subjected to physical and chemical processes to remove harmful contaminants and restore its conditions for drinking.
In these installations, piping must be approved for potable water applications, which confirms it will not contaminate the water it is meant to transport. Corrosion resistance is also critical to the long-term reliability of the line.
Corzan CPVC is NSF 61 and NSF 14 certified, confirming its use for potable water applications.
Reclaimed Water
As usable and potable water becomes an increasingly precious commodity, the importance of sustainable water management grows for the chemical processing industry. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), the most widely used sustainable building rating system in the world, incentivizes facilities of all types to be green. Water efficiency is an important part, and reclaiming water achieves it.
All types of piping materials have been used for reclaimed water transport, but none provide the balance of reliability, versatility and cost-effectiveness like CPVC. Corzan CPVC:
- Can be used above or below grade.
- Is certified for use as return air plenums.
- Resists internal and external corrosion.
Eye Wash and Shower Stations
All CPI facilities and labs are required to have eye wash and shower stations due to the chemicals involved in their processes. Installation is sometimes an afterthought, but if ever called upon, these stations must be operable and ready to transport portable water safely.
Do not overlook the many concerns related to eye wash and shower station piping—corrosion, biological growth (e.g. Legionella), high pressures and high temperatures. They also may account for thousands of feet of piping, so material, installation and lifecycle costs should be major considerations.
Many available materials present serious downsides:
- Steel is susceptible to corrosion from water, often causing clogs or plugs in the stations.
- PVC may be a cheaper option, but has limited pressure and temperature capabilities.
- Other plastics, such as HDPE, may offer corrosion resistance and the temperature and pressure capabilities needed, but come at a higher price point.
The best option is Corzan CPVC due to its:
- Exceptional resistance to corrosion from water.
- Biofilm formation resistance.
- Suitable temperature and pressure capabilities.
- Cost-effectiveness thanks to the low material costs and its easy installation.
Demineralized/Reverse Osmosis (DI/RO) Water
DI/RO water systems are used to control reactions, such as pH or concentration levels. These systems can feed reactions, supply laboratory experiments with consistently controlled feedwater or provide a controlled water supply.
In terms of piping metallics are occasionally used for DI/RO water systems, but are unable to sustain over the long run due to the water’s pH and purity level. Metals are prone to leaching, corrosion and biological contamination in this environment.
Many plastics—including PVDF, PVC and polypropylene (PP)—have been specified in these applications. Depending on the purity levels required, PVC or PP may not suffice. And compared to PVDF, CPVC provides significant cost savings and versatility, as it can be used in return air plenums.
Condensate Water Transfer
Recycle, reclaim and reuse systems all aim to use waste from one process to feed another. Saving a few cents a minute in production can result in hundreds of thousands in savings each year.
One way plants save energy and fuel consumption costs is by reusing hot condensate. After water is heated to steam, heat can be maintained when the water condenses back to a liquid form. Condensate can be reused in many different ways, including:
- As heated feedwater, by sending hot condensate back to the boiler’s deaerator.
- As pre-heat, for any applicable heating system.
- As steam, by reusing flash steam.
- As hot water, for cleaning equipment or other cleaning applications.
Piping in condensate water transfer systems must be corrosion resistance and perform at elevated temperatures. Metal delivers high temperature resistance, but is not recommended due to corrosion concerns with the water. Plants that use carbon steel systems require frequent replacement due to the corrosive nature of condensate to steel.
When considering plastics, they must be able to handle temperatures up to 200°F (93°C). Corzan CPVC is recommended for use up to 200°F (93°C) in pressure applications and up to 220°F (104°C) for non-pressure applications. Corzan CPVC has a heat distortion temperature (HDT) rating greater than 230°F (110°C) which is 20°F (10°C) higher than other CPVC compounds and also offers the superior corrosion resistance needed to keep it in place for decades.
Facility Unloading Stations for Key Acids and Bases
When a facility receives chemicals via railcar or tank truck, lines are used to unload the source and transfer its contents to a storage tank. These lines must be compatible with a wide range of chemicals of different pH levels and concentrations. CPVC’s breadth of chemical resistance is undeniable. It is extremely resistant to most acids, bases and salts, allowing its use for versatile, long-term use in applications such as facility unloading stations.
Corzan® CPVC Chemical Resistance
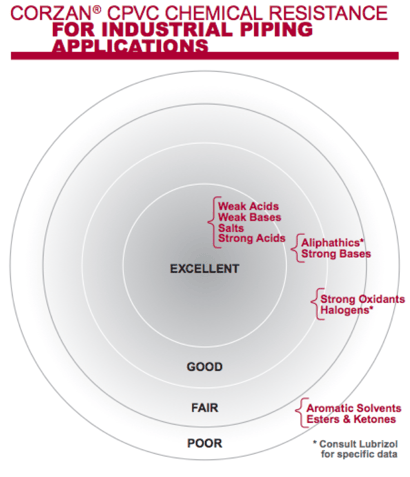
To see data on Corzan CPVC’s compatibility with more than 400 chemicals and compounds, view our Chemical Resistance Table.
Process Transfer Lines or Injection Lines for Acids and Bases
From the storage tank, chemicals and compounds are transported throughout a chemical processing plant to the various production areas via a process transfer line. From there, those chemicals are injected into various lines for use.
Because of their familiarity with metals, plants may trust carbon steel or certain grades of stainless steel. However, when interacting with a wide variety of chemicals, metals are prone to corrosion and often require premature replacement.
By specifying CPVC, plants can feel confident that these lines will remain reliable for years. The chemical resistance offered consistently across each product, coupled with superior temperature and pressure capabilities to other plastics, makes Corzan CPVC the obvious choice for transfer lines or injection lines.
Is CPVC Right for Your Chemical Processing Plant?
CPVC offers advantages across CPI applications. For dealing with the often corrosive and high-temperature environments of these plants, know that not all CPVC is created equal.
As with all materials, quality matters.
When compared to generic CPVC, Corzan CPVC testing confirms better consistency and performance in terms of:
- Minimum burst pressure requirements
- Dimensional tolerances
- Residual stress requirements
- Drop impact requirements
- Fusion property testing
- Pressure and temperature capabilities
- Higher Cell Class 24448 availability (for pipe available up to 8 in.)
Due to our intense quality controls and superior compound, the high performance characteristics of Corzan CPVC are consistent regardless of which partner manufacturer creates it, when it is manufactured or which region of the world it comes from.
Corzan Industrial Systems has a proven track record of dependable service in CPI applications. Our specifically engineered material provides an excellent balance of properties to improve reliability and user confidence. It reduces capital and life-cycle costs, and, most importantly, allows chemical plants to avoid unnecessary shutdowns and stay more productive.
To determine if Corzan CPVC is right for your plant or any specific plant system, please schedule a free consultation with our technical support team. They can provide a free process suitability review and offer an honest assessment of whether our material can satisfy your plant’s needs.




