An introduction to CPVC for hydrometallurgy
Our ever-increasing dependence on machines and technology, especially consumer electronics, has spurned innovation in the technical processes in which we recover essential materials.
Hydrometallurgy is one such process in which we recover and restore essential metals and minerals for everyday applications, such as rechargeable batteries, mobile phones or other electric and electronic devices.
Naturally, this is an intensive chemical process, in which the process installation materials are at risk of corrosion. The extreme conditions in which this process is implemented require suitable materials, as our dependency on technology increases.
Read on and learn more about the role of Corzan CPVC in this crucial process and its suitability in a growing industry. Download the free infographic at the bottom of this page for quick reference to this process and the benefits of CPVC.
Metal recovery processes explained
Hydrometallurgy is, in essence, the separation of materials through chemical and mechanical processes to extract valuable metals in their purest form. These materials go on to serve a variety of applications in modern society.
The extraction of metals, both common and rare, must be captured efficiently and sustainably in order to achieve the highest purity for high-quality metal products. It is an intensive process using aggressive chemicals, therefore it requires purpose-built solutions for safe, efficient and economically suitable extraction.
Sustainable solvent extraction and metal recovery
Hydrometallurgy is sustainable from both an environmental and operational point of view.
For example, the practice of reclaiming useful raw metals from urban waste has a positive impact on our environment, as opposed to classical mining which risks contaminating the natural environment. It boosts independence for the individual countries that employ it; mining their own waste products for valuable resources.
Furthermore, it reduces the reliance on dangerous, polluting and unethical working practices, such as those demonstrated in third-world countries where labour conditions are harmful to those involved in mining.
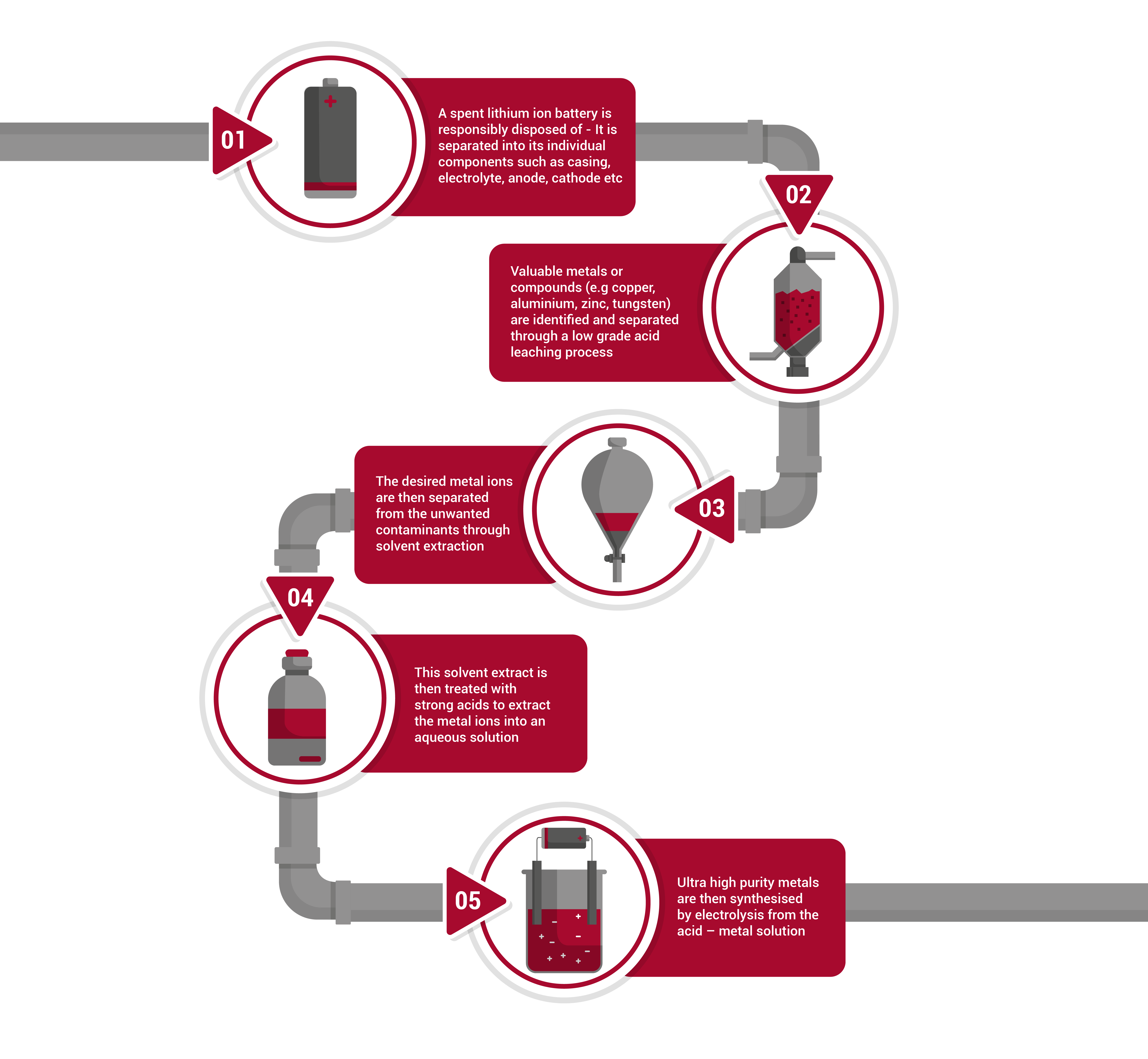
Let's look at the hydrometallurgical process in the processing of e-waste:
- A spent lithium-ion battery is responsibly disposed of
It is separated into its individual components such as casing, electrolyte, anode, cathode etc - Valuable metals or compounds (e.g copper, aluminium, zinc, tungsten) are identified and separated through a low grade acid leaching process
- The desired metal ions are then separated from the unwanted contaminants through solvent extraction
- This solvent extract is then treated with strong acids to extract the metal ions into an aqueous solution
- Ultra high purity metals are then synthesised by electrolysis from the acid–metal solution
Challenges achieving the desired metal component
Leaching solution concentration levels
The leaching process necessary for metal recovery is using highly corrosive acids. Further purification and electrolysis take place in the same corrosive environments. Handling the leaching solution and managing the downstream purification and electrolysis fluid stream concentration safely requires built-in chemical resistance.
Solvent extraction is key to achieving purity
In the metal recovery process, after acid leaching comes solvent extraction, to separate the desired metal component from the undesirable metal ions.
Successful metal recovery is, therefore, dependent on a number of conditions that processing materials must be prepared for: the temperature and concentration of the leaching acids and metal ion solutions.
What is CPVC pipe?
Corzan CPVC provides an industrial pipe and fittings solution to the chemical processing industry that is optimised for highly corrosive environments, such as hydrometallurgy processing.
Chemical processing plants, such as those responsible for the repurposing of e-waste, are notorious for highly corrosive, challenging industrial environments. The use of highly corrosive processing and extracting agents, (such as those used in hydrometallurgy like sulfuric acid) is a constant strain on mechanical integrity and financial upkeep.
Corzan CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride) is a thermoplastic specifically engineered for chemical processing applications worldwide.
Since CPVC pipe has a higher temperature resistance thanks to its increased concentration of chlorine atoms protecting its carbon chain from chemical degradation, it can be installed in high temperature environments requiring chemicals, where PVC pipework cannot be specified due to its thermal limitations (at 60°C in simple water.)
Its inherent chemical inertness, combined with its temperature and pressure resistance has made it the choice of chemical processing facilities worldwide, in particular where PVC or polyolefins can’t be used for temperature restrictions or where PVDF would be overengineered and too costly.
CPVC in recovering metal ions
- Leaching efficiency - CPVC's naturally high chlorine content is more suited to handling the extraction solutions of metals suitable for recovery.
- Resilience - Refining time varies from one material to another. Some targeted metals require prolonged exposure to leaching chemicals like Sulfuric acid (H2SO4.) Corzan CPVC has excellent chemical resistance characteristics in these situations, minimising life cycle costs.

Download your free infographic by completing the form below: