How to Combat Boiler Feed Water Scale and Corrosion
Effective feed water processing is an essential part of any boiler system, especially when the boiler is used in power generation.
Feed water processing requires corrosive solutions that can eat away at and weaken metal materials. In addition, other chemicals are used that can cause scaling within the system, choking off the flow of water and increasing pressure.
In the case of power generation, another major and unique concern is the efficacy and lifetime of the turbine blades. During power generation, the boiler creates the steam that turns the generator turbine, but if this steam contains impurities or hardness from boiler feed water, it can cause corrosion and scale on the blades.
To ensure the efficiency and long-term performance of your power generation system, our product and engineering team developed this post to walk through how boiler feed water treatment systems typically work, and call out the areas that can be problematic to metal piping systems.
How Boiler Feed Water Treatment Works
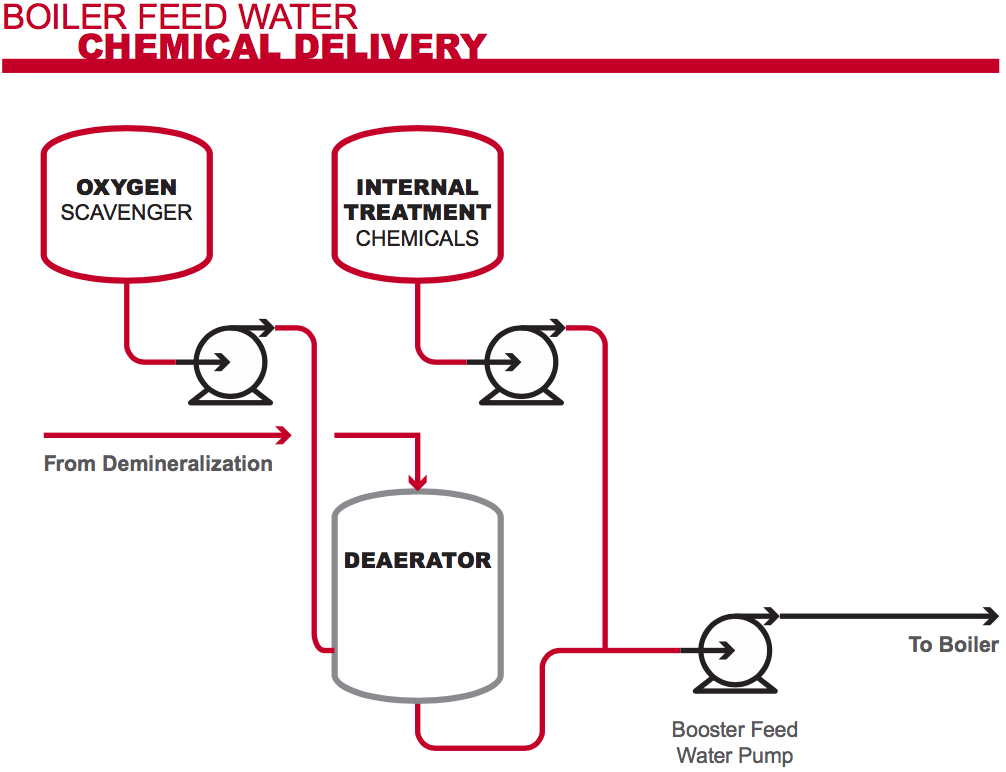
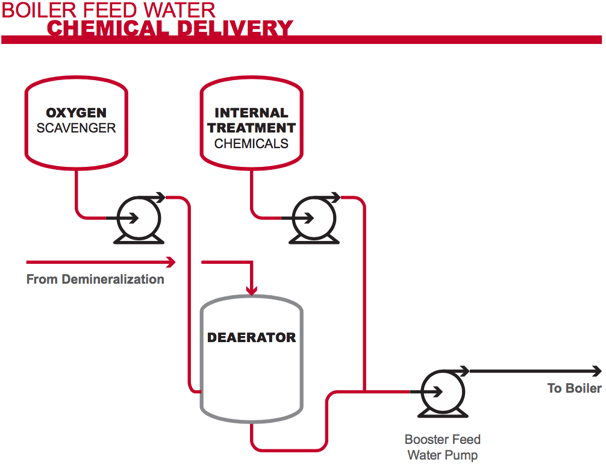 The above diagram shows a boiler feed water treatment system. The red indicates where CPVC pipes, fittings and liners can be used to improve the life and effectiveness of the system.
The above diagram shows a boiler feed water treatment system. The red indicates where CPVC pipes, fittings and liners can be used to improve the life and effectiveness of the system.
Proper boiler feed water treatment involves effective and reliable delivery of chemicals to remove corrosive substances, balance pH levels, and limit the conductivity of boiler water.
Specific treatment chemicals are introduced into the feed water at strategic points to remove the substances that tend to cause corrosion and scaling. These treatment chemicals include:
- Oxygen Scavengers: Sulfite-based oxygen scavengers remove any trace of oxygen that remains after the water has passed through the deaerator. Oxygen is a catalyst for corrosion.
- Scale Inhibitors: Phosphates are introduced into the boiler feed water stream to bind to the calcium ions and keep them from binding to metal parts, which can lead to scaling.
Boiling Feed Water Solutions
The material used for tank liners and piping in which treatment chemicals are stored and delivered is a very important consideration, particularly in power generation systems. Chemically treated water threatens the strength, flow rate and pressure of these systems without the proper material, because:
- Sulfites in high concentrations can be corrosive to many common types of metallic materials.
- Acid phosphate solutions that are fed neat can be corrosive to metallic feed systems. Orthophosphate treatments can produce deposits in the feed line.
Corzan® CPVC is ideal for boiler feed water systems. The material’s nonmetallic construction eliminates corrosion and scaling concerns, as well as any chance of re-introducing metal to the feed water stream after treatment.
Boiler Feed Water and CPVC Piping Compatibility
Making the decision to try new tank liners and piping can be challenging without reliable advice. While Corzan CPVC is effective for many applications, there are specific scenarios were other materials may offer a better option.
You can assess your boiler feed treatment chemicals with Corzan CPVC's compatibility by viewing our Chemical Resistance Table, which lists more than 400 chemicals and compounds.
Also, our team of product and engineering specialists are available for a free consultation. We're happy to discuss your boiler feed process and answer any questions you have about the viability and effectiveness of Corzan CPVC.