Corzan CPVC Can Take The Heat
The heat is on for piping systems installed in most industrial environments – in the form of high temperatures, elevated pressure, thermal cycles, excess heat generated by the sun and the heat of exotherms resulting from process upsets and operator error. Fire is also a hazard in many industrial applications, and especially within the chemical processing industry, and requires engineered systems with properties such as ignition resistance, burning resistance and flame spread resistance to help keep workers safe and limit property damage in the event of a fire.
Specially engineered Corzan CPVC® industrial systems are made to withstand the heat common to industrial environments. Piping, valves, ducting and tanks deliver reliability, a longer service life, less maintenance and reduced downtime to ensure a facility’s productivity and long-term performance.
Successful Operation with High Temperatures and Elevated Pressure
Metal piping has long proven its ability to satisfy the heat and pressure requirements for many industrial piping applications. As more designers specify non-metallic piping systems, however, industries within the U.S. rely on ASTM D2837, the Standard Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Products, to determine a piping material’s pressure-bearing capability.
The test subjects piping product samples to a range of pressures that will cause the pipe to rupture at various times – from a few hours to over 10,000 hours. The graphic that follows shows the actual temperature and pressure levels at which Corzan CPVC may be successfully operated compared to the perceived usable range.
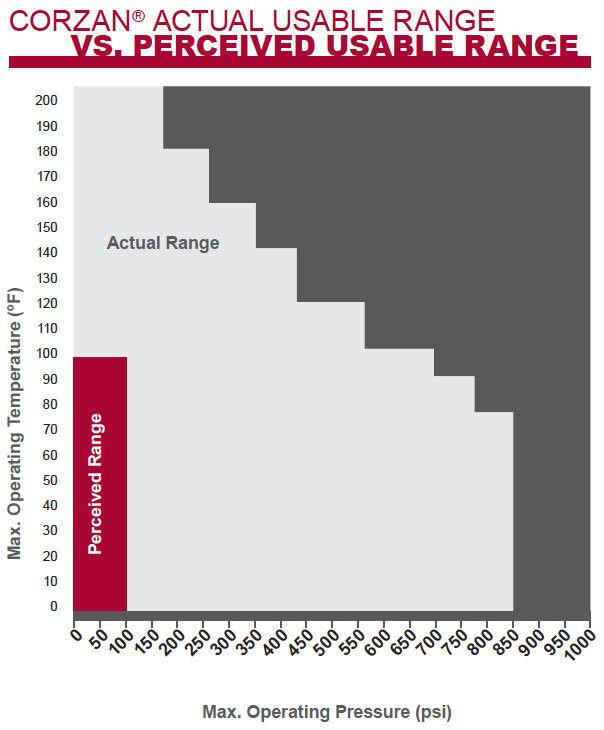
Corzan CPVC provides pressurized service up to 200°F and has a higher pressure rating during most of its useful temperature range than most thermoplastic materials specified for industrial piping. The material is also well suited to many process applications as a result of its outstanding resistance to many corrosive chemicals at temperatures up to 200°F. The Corzan CPVC Chemical Resistance Chart compare’s the material’s compatibility against over 400 chemicals.
Fire Resistance for Improved Safety and Productivity
A fire has the potential to turn an industrial facility into chaos and create life-threatening situations. For this reason, designers and engineers should specify fire safe piping, evaluating systems for properties such as a high flash ignition temperature, burning resistance and flame spread resistance. Excellent fire performance and low thermal conductivity are required for a material to achieve a FM4910 designation as fire safe. Corzan CPVC has helped create a safe environment in a wide range of industrial process piping and ducting applications.
Ignition resistance
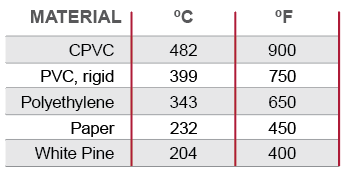
A piping system’s flash ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a small external flame will ignite combustible gas. Corzan CPVC has a flash ignition temperature of 900°F compared to 650°F for polyethylene.
The chart that follows provides the flash ignition temperature for several thermoplastics and other materials.
Flash Ignition Temperature Comparison
 Burning resistance
Burning resistance
A material’s burning resistance is measured using the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI), which is the percentage of oxygen needed in the surrounding atmosphere to sustain a flame. Corzan CPVC has a high LOI of 60 percent, which means it will not supply fuel for a fire in the form of oxygen under normal atmospheric conditions. The earth’s atmosphere, in comparison, is comprised of 21 percent oxygen.
The instant a flame is extinguished from around Corzan CPVC piping, the material will self-extinguish and the burning will stop. A burn test was conducted to confirm Corzan CPVC piping’s response to flame. The video that follows shows how the material develops a protective char immediately after it is exposed to fire. This charring acts as a thermal barrier to reduce the rate of burning.
Other thermoplastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene will continue to burn after the flame is extinguished.
Building codes restrict the surface burning characteristics of materials that can be installed in air plenums, with the construction materials permitted in plenums required to meet a 25/50 flame spread/smoke developed when tested in accordance with ASTM E84. Corzan pipe and fittings meet the 25/50 flame spread and smoke developed requirements of the International Mechanical Code (IMC) and the Uniform Mechanical Code (UMC) for installation in plenums when tested in general accordance with ASTM E84. In addition, Corzan CPVC meets the 25/50 ULC CAN-S102.2 Surface Burning Characteristics for use in return air plenums.
Flame spread resistance
A material’s flame spread resistance is important as it helps keep flames contained so firefighters or extinguishing systems can more quickly quench a blaze and minimize property and equipment damage. Corzan CPVC’s flammability is tested in accordance with UL 94, which determines the flammability of plastic materials used in parts and components of finished products.
The test specifically measures a material’s resistance to burning, dripping, glow emission and burn through. Corzan CPVC achieved the highest available burn rating within the scope of this test of VO, 5VB and 5VA.
Factory Mutual developed the standard FM 4910 for the semiconductor and electronics industry. The standard requires materials to provide greater resistance to flame and smoke development to limit the damage than can result from fire.
Corzan CPVC compounds were evaluated and pass the FM 4910 test protocol for fire propagation and smoke development. These compounds include gray duct compound, gray pipe compound and Corzan 4910 compounds.
Low thermal conductivity
Extreme heat can start a fire if sufficient fuel and oxygen are present. While firewalls are designed to stop the spread of flame and smoke throughout a building, they cannot prevent heat from transferring through the piping system and starting a fire in another area.
Metal piping has a high thermal conductivity and transfers heat very well. Corzan CPVC’s thermal conductivity is low and will limit the transference of heat through firewalls.
Weatherability to Withstand the Elements
Many industrial piping systems are partially or completely installed outdoors, exposing the systems to temperature extremes and direct sunlight. While some thermoplastics are able to withstand the effects of ultraviolent radiation on piping, other systems cannot tolerate direct sunlight. Prolonged UV exposure causes some thermoplastics to chemically break down, resulting in early degradation and a shorter system life.
Corzan CPVC is UV resistant and incorporates significant quantities of carbon black and titanium dioxide (TiO2), which are excellent ultraviolet blocking agents. These additives protect the pipe’s polymer backbone and enable it to retain its pressure bearing capability even after extended UV exposure.
The graphic below illustrates the effect that direct sunlight has on the Corzan CPVC surface temperature compared to other piping system materials.
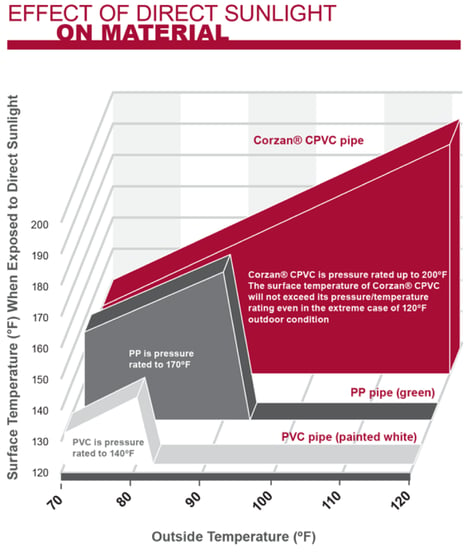
Depending on the installation, additional protection from UV radiation may be obtained by painting the piping with water based latex paint. Lubrizol’s partner manufacturers are the best resources to determine whether protective paint is necessary for a specific application.
Piping systems must also be able to withstand extreme radiant heat as radiant heat in combination with ambient temperature can push a piping material beyond its heat deflection temperature (HDT), which is the measurement that is commonly used to determine a piping system’s maximum use temperature.
At 230°F (110°C), Corzan CPVC Cell Class 24448 materials have the highest HDT in accordance with ASTM D1783 of any certified CPVC material. In comparison, standard CPVC has an HDT of 212°F (100°C).
Durable Industrial Piping Engineered to Perform with High Heat Levels
Corzan CPVC is the most specified CPVC technology in the world, offering mechanical strength and properties such as fire performance and weatherability that make it a safe and durable alternative to metal for a range of industrial applications. The material also tolerates high temperatures and elevated pressures common to industrial environments and provides three times the impact strength of standard CPVC, resulting in fewer fractures and breaks and ultimately less maintenance and lower life-cycle costs.
Corzan industrial piping systems have successfully provided products for industrial applications worldwide for nearly 60 years. Contact a Corzan engineering expert or one of our partner manufacturers for engineering guidelines to specify a safe and reliable piping system or to schedule a free process suitability review and technical assessment.
Details for this blog were taken, in part, from the following:
https://www.corzan.com/en-us/piping-systems/specification/fire-performance
https://www.corzan.com/blog/what-does-it-mean-for-a-pipe-to-be-fire-resistant
https://www.corzan.com/en-us/piping-systems/specification/weatherability
https://www.corzan.com/blog/what-you-need-to-know-about-cpvc-and-uv-weatherability