What You Need to Know About Supports and Hangers for CPVC Piping and Ducting
For any industrial piping or ducting system, it is critical that hangers and supports are correctly spaced. Too much space between supports adds unnecessary stress to your system, causing deflection and sagging. Too little spacing, and you will incur unnecessary expenses.
An advantage CPVC has over other thermoplastics is that at elevated temperatures it maintains its structural integrity, requiring fewer supports. Depending on the size of the system, this can create significant advantages across material, design and—most importantly—labor costs.
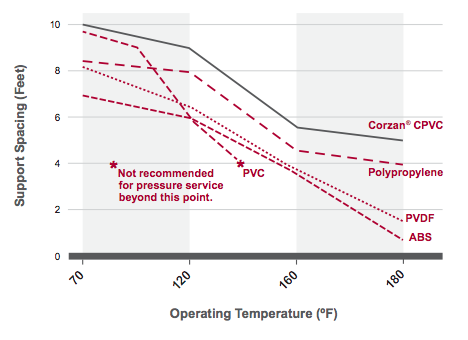
CPVC is more efficient than other thermoplastics
Although required support spacing is less for CPVC than other thermoplastics, it is not as rigid as traditional metal piping systems, requiring additional supports. However, in corrosive applications, the additional hangers are a small price to pay for extended system reliability.
Ultimately, the number and spacing of hangers and supports will be determined by the system conditions and piping or ducting requirements.
Factors Affecting the Distance Between Hangers and Supports in CPVC Systems
The factors determining appropriate spacing for hangers for any material, including CPVC, include duct/piping diameter, system temperature rules, weight of the liquid being transported, location of concentrated loads and places where buildup could form in pipes. There is no single spacing rule for all applications. Always check with the manufacturer's manual for correct spacing for your application.
- Duct/piping diameter. Larger diameter piping or ducting is inherently less prone to deflection, allowing for fewer supports.
- Temperature parameters of the system. As temperature increases, the material stiffness or flexural modulus of thermoplastics decreases, requiring more frequent supports.
- Weight of transported liquids. Denser processing chemicals and solids will increase demands on the piping, creating the need for more supports.
- Location of concentrated loads. To help support the weight of heavy instruments or valves in the system, additional supports may be employed.
- Possibility that process solids/liquids accumulate in the system. To prevent sagging of the pipe, processes prone to weight buildup from solids or liquids should consider increasing the number of supports.
Support and Hanger Spacing for CPVC Piping Systems
Taking into account the three fundamental factors—pipe size, pipe schedule and processing temperature—we have developed the maximum support spacing tables for Corzan® CPVC. The table assumes:
- Straight runs of uninsulated lines.
- Systems conveying fluids with specific gravities up to 1.0.
- Allowing for minimal to no sagging of the pipe.
If your system conveys liquids of higher specific gravities, you’ll need to multiply the number you see on the table by the corresponding number from this table:
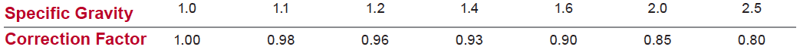
As expected, schedule 40 piping, which has a thinner pipe wall, requires more frequent supports than schedule 80. Piping with a thinner wall is inherently more flexible and prone to sagging if appropriate support distances are not followed.
Maximum Support Spacing for Schedule 40 CPVC Piping (in feet)
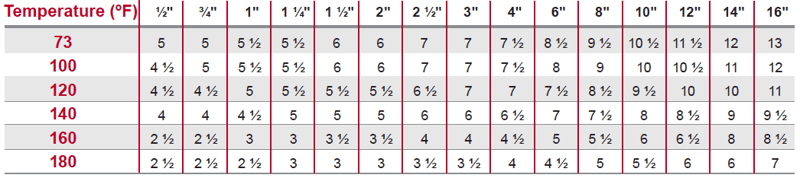
Maximum Support Spacing for Schedule 80 CPVC Piping (in feet)
-1.png?width=800&name=Maximum-Support-Spacing-Schedule%20(1)-1.png)
Vertical runs of pipe should be supported every 10 feet.
Tips for Installing CPVC Piping System Supports and Hangers
While the recommended support distances are provided for straight runs, industrial systems are not solely comprised of straight runs of pipe. Valves, flanges, bends, tees, joints, and other heavy components may require independent support in CPVC systems. Add additional supports for straight runs when necessary and assure that you don’t go over the recommended distance between supports.
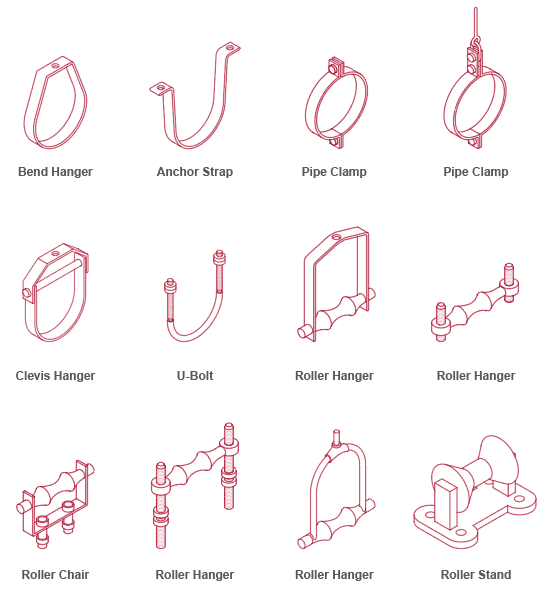
When choosing hangers, clamps, or supports, ensure the right fit for the situation and provide the necessary support. Bare metal pipe hangers without sharp edges can be used with CPVC pipes and are particularly useful in supporting lengths of pipe with heavy loads. Also, be especially careful that edges are smooth/rounded to negate the chance the pipe will be scratch or abraded by the support or hanger. Not forcing fittings into place or over tightening them will also help keep piping free from harm.
Recommended options include the following:
Support and Hanger Spacing for CPVC Ducting Systems
Though CPVC ducting has a thinner wall than schedule 40 or 80 piping, it requires fewer supports because of the relative weight of what is being conveyed.
Below are the recommendations for support spacing in Corzan CPVC ducting systems (in feet).
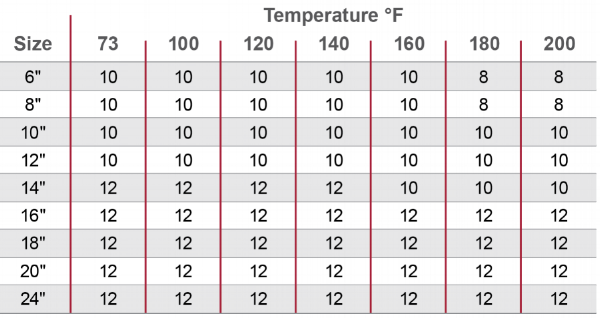
As is true of piping, vertical duct runs should be supported by guides every 10 feet.
CPVC ducting must also be independently supported at heavy points to ensure the highest system integrity. These include:
- Fans
- Flexible connections
- Hoods
- Scrubbers
- Tanks
- Other system components
Similar to CPVC piping systems, support your ducting at each of these heavy points and add additional supports for straight runs where necessary.
Finally, in case of CPVC thermal expansion, avoid over-tightening supports or using supports with sharp or abrasive edges.
Learn How to Account for Thermal Expansion in Piping System Design
In addition to planning for support and hanger spacing during system design, make sure to consider thermal expansion. In this blog post, our team takes an in-depth look at thermal expansion and contraction, providing:
- The four design factors involved.
- The four piping system deflection mechanisms and how they work.
- An easy-to-use calculator for determining thermal expansion loops for your system.



